Versal PL NVMe SSD Speed Test
Using Versal AI Edge Series VEK280

Posted on December 2, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
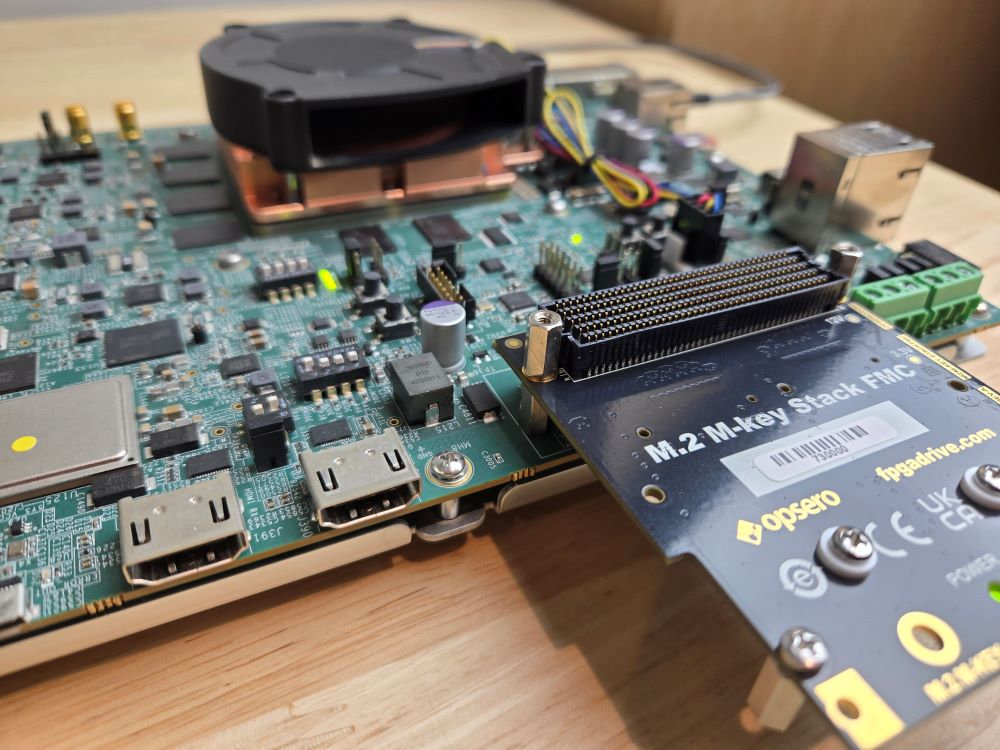
Hands down, the best solution for non-volatile storage on Versal designs, is NVMe solid-state drives. One of the main reasons why they are such a good fit is because they interface with the host device over PCI Express. Versal Prime, AI Core and AI Edge devices all have integrated PCIe blocks, and most of them are PCIe Gen5 compliant. This means that there are no extra IP costs to connect an NVMe SSD to the Versal devices because everything you need is already built into the device.
[Read More]
Multi-port 25G Ethernet on Versal ACAP
A reference design that you can build and test
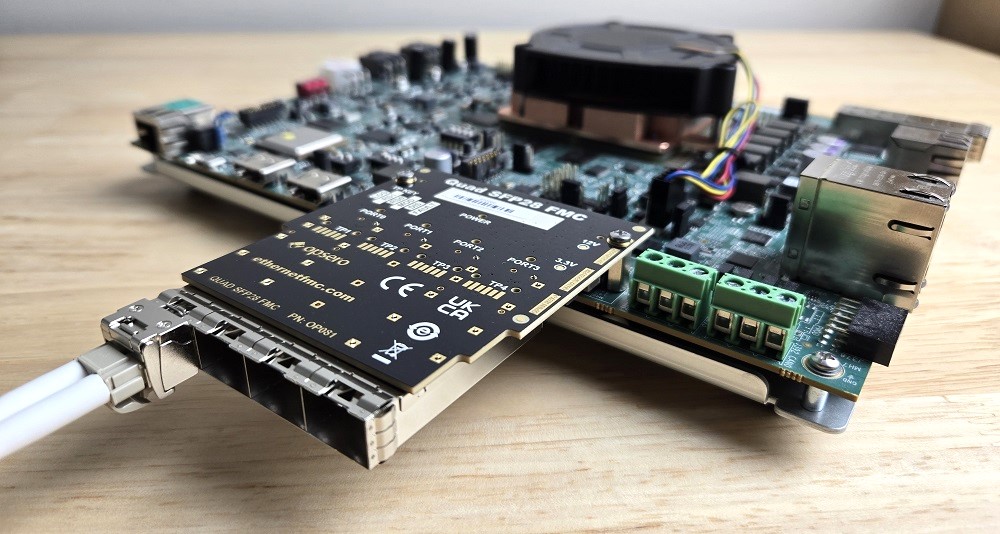
Posted on October 8, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
In this post we’re going to build and run our new multi-port 25G Ethernet reference design for Versal boards and the Opsero Quad SFP28 FMC. The design is based on the AMD Xilinx 10G/25G Ethernet Subsystem IP. Specifically, we’re going to boot PetaLinux on the VEK280 and establish a 25G Ethernet connection between it and a 25G network adapter that is installed in a Ubuntu PC. We’re doing this on Versal board VEK280 which is one of the few AMD FPGA-containing devices that can support 25G Ethernet at the time of writing.
[Read More]
How to Install Vitis and PetaLinux 2024.1
For Ubuntu 20.04

Posted on July 2, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
Here we go again. In this post I’m going to go through the steps of installing Vitis and PetaLinux 2024.1. Unfortunately I have to go through this process on a regular basis. Installing dev tools like this from the biggest FPGA vendor in the world should be easy but for some reason there are always problems - hence the need to keep notes.
The image that I used for this post was generated by ChatGPT.
[Read More]
Enabling VADJ on Versal VCK190 and VMK180
Posted on March 21, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
Important This workaround is applicable to the VCK190, VMK180 and VPK120 because they all use the same circuitry for generating the VADJ voltage: an IR38164 buck regulator with the same I2C address (0x1E), connecting to the same port of the same I2C switch (address 0x74, port 0) and connecting to the same I2C pins of the Versal device (PMC MIO46/47).
Note that this workaround is NOT applicable to the VEK280 because that board applies a fixed VADJ voltage of 1.
[Read More]
Using NVMe SSDs with Versal VCK190 and VMK180

Posted on March 18, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
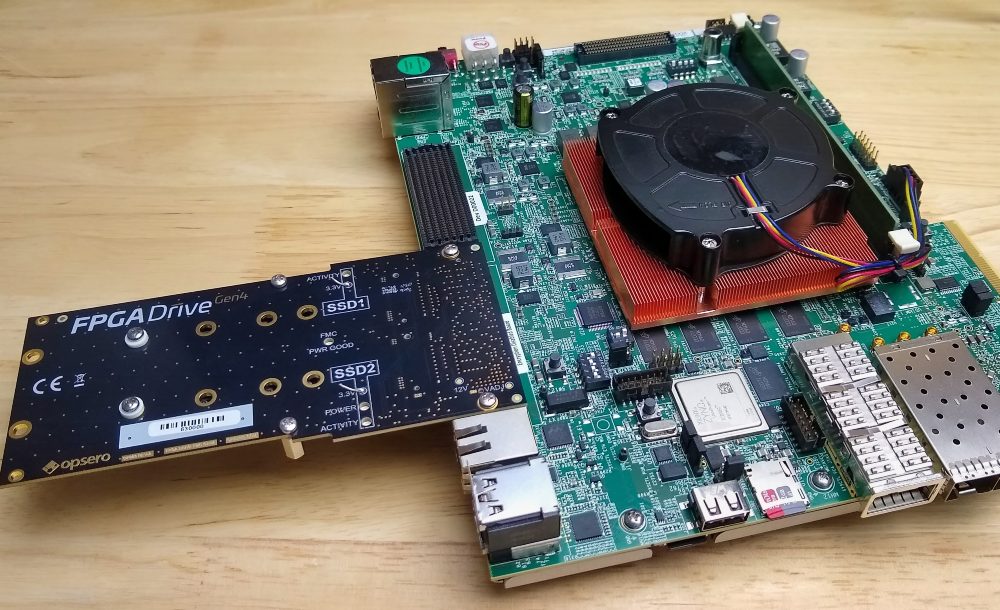
High-capacity non-volatile storage is pretty handy in the intensive computing applications that the Versal ACAP adaptive SoCs get employed in. NVMe SSDs are a perfect way to provide that storage because they can directly interface with the Versal’s integrated blocks for PCIe. Those integrated blocks are Gen4 compliant which makes for an extremely high bandwidth connection between the FPGA fabric and the storage medium.
Over the past couple of weeks, my team and I have been bringing up an NVMe SSD on the Versal AI Core VCK190 Evaluation kit using the FPGA Drive FMC Gen4 adapter.
[Read More]
Multi-camera YOLOv5 on Zynq UltraScale+ with Hailo-8 AI Acceleration

Posted on February 15, 2024
| Jeff Johnson
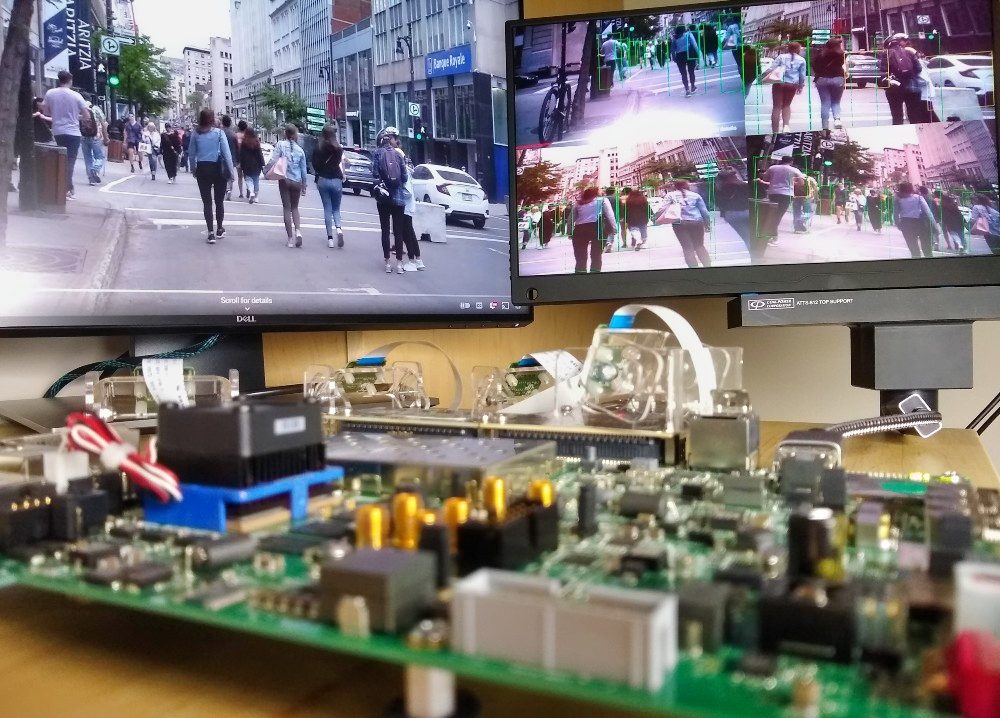
See it live: The demo described in this post will be displayed live at the EBV Elektronik booth at Embedded World 2024 on April 9-11. I’ll be attending too, so get in touch if you’re keen to meet up. Over the last few months I’ve been lucky to work with two very talented people on an interesting project for multi-camera machine vision applications: Gianluca Filippini and Mario Bergeron. Back in 2022, I was contacted by Gianluca, an engineer from EBV Elektronik.
[Read More]
Change the temp folder used by PetaLinux

Posted on November 8, 2023
| Jeff Johnson
When working with PetaLinux tools, we need to be wary of the often very sizeable temporary files generated during builds. These temporary files can often take up more than 10GB, and they are crucial for the build process.
By default, PetaLinux tools create a temporary folder internal to the project directory. Having it set this way is useful because our projects are well contained and we have clear insight into the total disk space used by a project.
[Read More]
How to build PetaLinux in offline mode
ie. without a network connection

Posted on October 10, 2023
| Jeff Johnson
In certain scenarios, you might want to build PetaLinux without relying on an active internet connection. This offline building feature can be useful for various reasons. To build PetaLinux without a network connection, you obviously need pre-downloaded source packages and dependencies. Xilinx allows you to pre-download all of these dependencies (called sstate cache artefacts) and then perform the build offline.
Why You Would Use It The reason to use offline mode really depends on your situation and it’s definitely not something that everyone will get benefit from.
[Read More]
Adding a script to the root file system in PetaLinux
And making it run on start-up

Posted on September 21, 2023
| Jeff Johnson
When designing custom PetaLinux builds, we often end up with a bunch of commands that we have to run after login to set things up and make initializations. Having a script built into the root filesystem can make this process easier, so in this post I’m going to show you how you can set that up in PetaLinux 2022.1.
These instructions assume that you already have a PetaLinux project created.
[Read More]
A Smart Camera implemented in PetaLinux 2022.1 on ZCU104
Using a Raspberry Pi camera

Posted on July 12, 2023
| Jeff Johnson
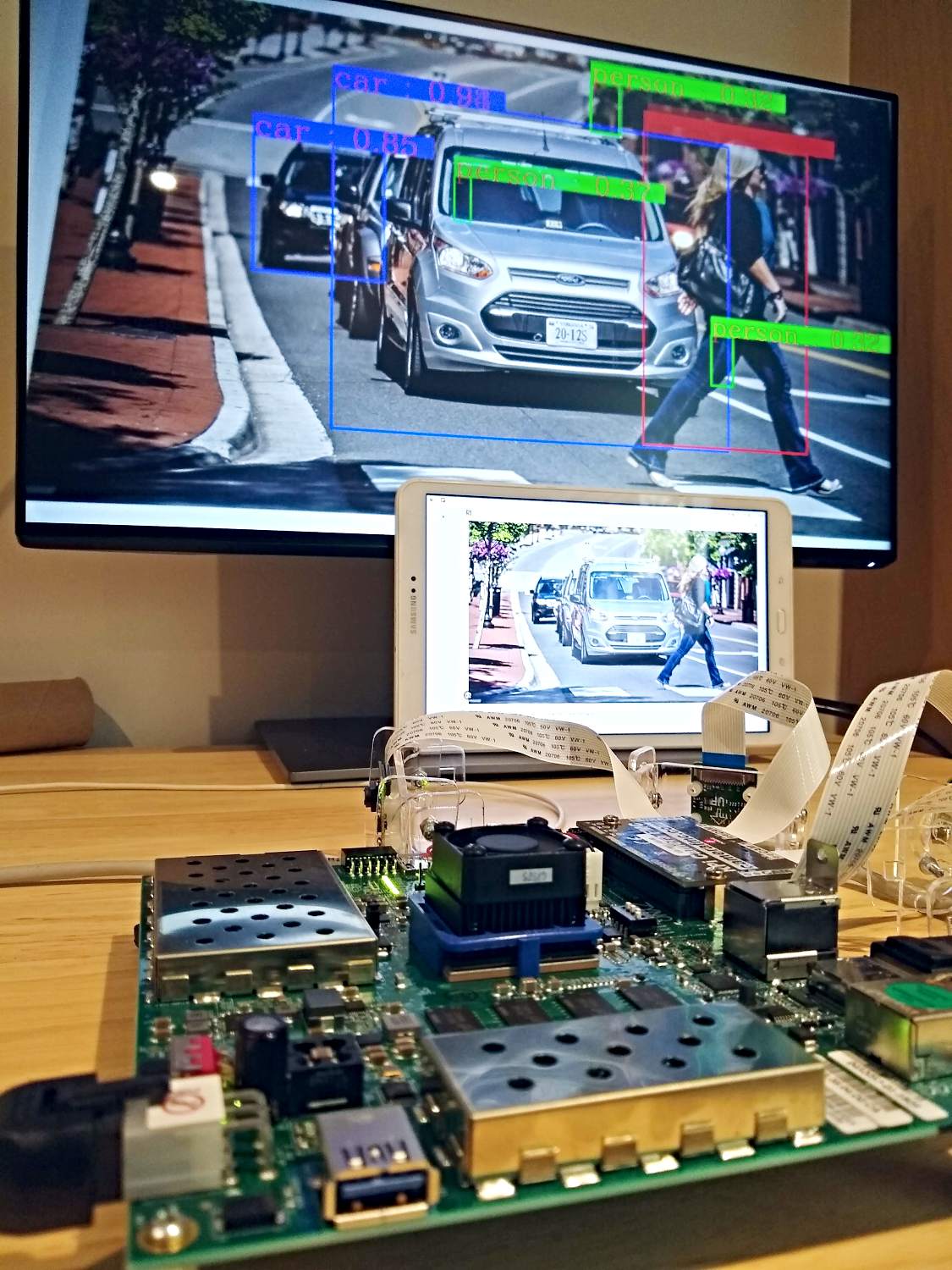
In this post we’re going to build a smart camera using a Raspberry Pi camera, the ZCU104 board and PetaLinux. We’re going to do this by leveraging the Smartcam app which was originally designed for the AMD Xilinx Kria SoM. Our version of the Smartcam app can take video inputs from a Raspberry Pi camera, a USB camera or a file, and it can output video to a DisplayPort monitor, a file or via Ethernet over Real-time Transport Protocol.
[Read More]










